What Does Tt Isle of Man Stand for
Annual motorcycle race held on the Isle of Man
"Isle of Man Tourist Trophy" redirects here. For a series of car races held on the Isle of Man between 1905 and 1922, see RAC Tourist Trophy.
 | |
|---|---|
| Isle of Man Tourist Trophy | |
| Region | Isle of Man |
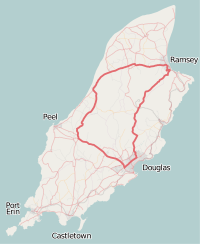
| Course | Isle of Man TT Mountain Circuit |
| Type | Public road course |
| Clerk of the Course | Gary Thompson MBE BEM |
| Event Organiser | ACU Events Ltd |
| Principal sponsor | Isle of Man Department for Economic Development |
| History | |
| First race | 1907 |
| Number of race meetings | 100 (to 2019) |
| First winner | C. R. Collier (1907) |
| Most wins | Joey Dunlop 26 (1977–2000) |
| Lap record | Peter Hickman 16m 42.778s – 135.452 mph (217.989 km/h) (2018)[1] |
The Isle of Man TT or Tourist Trophy races are an annual motorcycle racing event run on the Isle of Man in May/June of most years since its inaugural race in 1907. The event is often called one of the most dangerous racing events in the world.[2]
Overview [edit]
The Isle of Man TT is run in a time-trial format on public roads closed to the public by an Act of Tynwald (the parliament of the Isle of Man). The event consists of one week of practice sessions followed by one week of racing. It has been a tradition, perhaps started by racing competitors in the early 1920s, for spectators to tour the Snaefell Mountain Course on motorcycles during the Isle of Man TT on "Mad Sunday",[3] an informal and unofficial sanctioned event held on the Sunday[4] between 'Practice Week' and 'Race Week'.
The first Isle of Man TT race was held on Tuesday 28 May 1907 and was called the International Auto-Cycle Tourist Trophy.[5] The event was organised by the Auto-Cycle Club over 10 laps of the Isle of Man St John's Short Course of 15 miles 1,470 yards for road-legal 'touring' motorcycles with exhaust silencers, saddles, pedals and mudguards.
From 1911 the Isle of Man TT transferred to the much longer Snaefell Mountain Course of 37.40 miles (60.19 km) (current length 37.73 miles (60.72 km)). Its elevation goes from sea-level to 1,300 feet.[6] The race programme developed from a single race with two classes for the 1907 Isle of Man TT, expanding in 1911 to two individual races for the 350cc Junior TT motor-cycles and the Blue Riband event the 500cc Senior TT race. The race did not take place from 1915 to 1919 due to the First World War. It resumed in 1920. A 250cc Lightweight TT race was added to the Isle of Man TT programme in 1922, followed by a Sidecar TT race in 1923.
There was no racing on the Isle of Man between 1940 and 1945 due to the Second World War. It recommenced with the Manx Grand Prix in 1946 and the Isle of Man TT in 1947, with a greatly expanded format that included the new Clubman's TT races. The Isle of Man TT became part of the FIM Motor-cycle Grand Prix World Championship (now MotoGP) as the British round of the World Motor-Cycling Championship during the period 1949–1976. Following safety concerns with the Snaefell Mountain Course and problems over inadequate "start-money" for competitors, there was a boycott of the Isle of Man TT races from the early 1970s by many of the leading competitors, motorcycle manufacturers and national motorcycle sporting federations.[7]
It is still regarded in popular culture as the most dangerous motorsport event in the world, with the New York Times stating that the number of deaths has risen "to 146 since it was first run in 1907; if one includes fatal accidents occurring during the Manx Grand Prix, the amateur races held later in the summer on the same Snaefell Mountain Course, the figure rises above 250".[8] [9] An on-site account of the 2003 race by Sports Illustrated writer Franz Lidz called the spectacle "38 Miles of Terror... a test of nerves and speed that may be sport's most dangerous event."[10]
In 1976, the Isle of Man TT lost its world championship status; this was transferred to the United Kingdom by the FIM and run as the British Grand Prix for the 1977 season. The Isle of Man TT Races then became an integral part of the new style TT Formula 1, Formula 2 and Formula 3 World Championships between 1977 and 1990 to develop and maintain the international racing status of the Isle of Man TT races.[11]
The event was redeveloped by the Isle of Man Department of Tourism as the Isle of Man TT Festival from 1989 onwards. This included new racing events for the new Isle of Man TT Festival programme, including the Pre-TT Classic Races in 1989 followed by the Post-TT Races from 1991, both held on the Billown Circuit. In 2013, the Isle of Man Classic TT was developed by the Isle of Man Department of Economic Development and the Auto-Cycle Union for historic racing motorcycles, and along with the Manx Grand Prix now forms part of the 'Isle of Man Festival of Motorcycling' held in late August of each year.
There has been criticism of the event. In 2007 an incident during the Senior Race resulted in the deaths of a rider and two spectators.[12] The resultant inquest made several recommendations and included several comments, such as: 'Senior Marshals may well have been elevated beyond the sphere of their competence'.[13] The coroner also noted that "I am more than aware of the fact that the witnesses from the Manx Motor Cycle Club and the marshals are all volunteers. They give their time freely and without paid reward. Having said that however, if it were suggested because they were volunteers there should be some allowance in the standards expected of them, then I regret I cannot agree."[14]
In 2018, a solo competitor was seriously injured during a head-on collision with an official Course Car being driven at high speed when conveying police officers to officiate at the scene of a fatality further along the course. He was one of seven riders who had been halted on the course and turned back by marshals, being instructed to proceed back to the paddock area in the reverse-direction after the red flag stoppage.
In 2020, Isle of Man TT Races which were due to take place between 30 May and 13 June were cancelled as the island stepped up its measures to protect the population against the COVID-19 pandemic.[15] The pandemic also caused the cancellation of the 2021 TT races.[16]
Early Isle of Man TT race history (1904–1910) [edit]
Gordon Bennett and Tourist Trophy car races [edit]
Motor racing began on the Isle of Man in 1904 with the Gordon Bennett Eliminating Trial, restricted to touring automobiles. As the Motor Car Act 1903 placed a speed restriction of 20 mph (32 km/h) on automobiles in the UK, Julian Orde, Secretary of the Automobile Car Club of Britain and Ireland approached the authorities in the Isle of Man for the permission to race automobiles on the island's public roads.[17] The Highways (Light Locomotive) Act 1904 gave permission in the Isle of Man for the 52.15-mile (83.93 km) Highroads Course for the 1904 Gordon Bennett Eliminating Trial which was won by Clifford Earl (Napier) in 7 hours 26.5 minutes for five laps (255.5 mi or 411.2 km) of the Highroads Course. The 1905 Gordon Bennett Trial was held on 30 May 1905 and was again won by Clifford Earl driving a Napier automobile in 6 hours and 6 minutes for six laps of the Highroads Course. This was followed in September 1905 with the first Isle of Man Tourist Trophy Race for racing automobiles, now known as the RAC Tourist Trophy and was won by John Napier (Arrol-Johnston) in 6 hours and 9 minutes at an average speed of 33.90 mph (54.56 km/h).[18]
International Motor-Cycle Cup Race (1905) [edit]
For the 1905 Gordon Bennett Eliminating Trial it was decided to run an eliminating trial for motorcycles the day afterwards for a team to represent Great Britain in the International Motor-Cycle Cup Races. An accident at Ramsey Hairpin forced out one of the pre-race favourites, and the inability of the competitors to climb the steep Mountain Section of the course forced the organisers to use a 25-mile (40 km) section of the Gordon Bennett Trial course. This ran from Douglas south to Castletown and then north to Ballacraine along the primary A3 road and returning to the start at the Quarterbridge in Douglas via Crosby and Glen Vine along the current Snaefell Mountain Course in the reverse direction. The 1905 International Motor-Cycle Cup Race for five laps (125 mi or 201 km) was won by J.S. Campbell (Ariel) despite a fire during a pit stop[19] in 4 hours, 9 minutes and 36 seconds at an average race speed of 30.04 mph (48.34 km/h).[20]
Format of the races [edit]

The TT Races since the first race in 1907 have been in the format of time-trial. The races held on the Clypse Course during the period 1954–1959 were the more traditional full grid starts along with the 1924 Lightweight TT Race and Clubmen TT Races from 1948, which were also "mass-start" races. The current format is a "clutch start" and race competitors will be "started singly at 10-second intervals".[21]
Race procedure [edit]
- Start Preliminaries
- First Signal – 45 minutes before the start with a warm-up of engines in the Race Paddock and assembly area.
- Second Signal – 30 minutes before start.
- Third Signal – 15 minutes before start, race competitors move to the start-line and form-up in qualification order.
- Fourth Signal – 5 minutes before start, signal to clear the grid and race competitors move towards the exit-gate.
Eligibility [edit]
Entrants must be in possession of a valid National Entrants or FIM Sponsors Licence for Road Racing.
Entrants must cite pre-filled documentation of completion of a UK drivers licence or motorcycle certification or a drivers licence from a comparable country that is recognised by UK comparable department of transportation standards and may withhold due to any pre race or post race suspensions.
Race classes [edit]
- Current
- Senior TT (1909–present)
- Lightweight TT (1922-1976, 1995–2004, 2012-present)
- Junior TT / Supersport TT (1911–present)
- Superbike TT (2005–present)
- Superstock TT (2005–present)
- TT Zero (2010–present)
- Sidecar TT (1923-1925, 1951–1967, 1977-present)
- Former
- Singles TT (1907-1908, 1994–2000)
- Twin TT (1907-1908)
- Sidecar 1000 TT (1975-1976)
- Sidecar 750 TT (1968-1974)
- Sidecar 500 TT (1968-1976)
- Ultra-Lightweight TT (1924-1925, 1951–1974, 1989–2004, 2008)
- Clubman Senior TT (1947-1956)
- Clubman Junior TT (1947-1956)
- Clubman Lightweight TT (1947-1950)
- Clubman 1000 TT (1949-1950, 1953)
- 50 TT (1962-1968)
- Classic TT (1975-1984)
- Formula 1 TT (1977-2004)
- Formula 2 TT (1977-1987)
- Formula 3 TT (1977-1982)
- Production 1500 TT (1985-1985)
- Production 1000 TT (1974, 2002–2004)
- Production 750 TT (1967-1973, 1984–1985)
- Production 500 / 600 TT (1967-1974, 2002–2004)
- Production 250 TT (1967-1974, 1984–1985)
- Production TT (1975-1976, 1996–2000)
- Production A TT (1986-1988)
- Production B TT (1986-1988)
- Production C TT (1986-1988)
- Production D TT (1986-1988)
- Supersport 600 TT (1989-1994)
- Supersport 400 TT (1989-1994)
- Lightweight 400 TT (1999-2004)
- TTXGP (2009)
Superbike TT [edit]
The 2015 specification for entries into the Superbike TT race are defined as:
- Any machine complying with the following specifications:
- TT Superbike: (Machines complying with the 2015 FIM Superbike Championship specifications)
- Over 750 cc up to 1000 cc 4 cylinders 4-stroke
- Over 750 cc up to 1000 cc 3 cylinders 4-stroke
- Over 850 cc up to 1200 cc 2 cylinders 4-stroke
- TT Superbike: (Machines complying with the 2015 FIM Superbike Championship specifications)
Minimum Weight 165 kg (364 lb). Other machines admitted at the discretion of the Organisers[22]
Supersport TT [edit]
The 1911 Isle of Man TT was the first time the Junior TT race took place, open to 300 cc single-cylinder and 340 cc twin cylinder motorcycles, contested over five laps of the new 37.5-mile (60.4 km) Snaefell Mountain Course. The first event on the new course was the Junior TT Race contested by 35 entrants, won by Percy J. Evans riding a Humber motor-cycle at an average race speed of 41.45 mph (66.71 km/h). The 1912 event was the first to limit the Junior TT to only 350 cc machines and this engine capacity prevailed until 1976, after which the category was dropped. The event was instead run for 250 cc machines until 1994 when replaced by the 600 cc Supersport class.
-
- 1911 For single cylinder motorcycles not exceeding 300 cc engine capacity and 340 cc twin cylinder motorcycles.
- 1912–1948 For motorcycles not exceeding 350 cc engine capacity.
- 1949–1953 FIM World Championship event for motorcycles not exceeding 350 cc engine capacity and held on the Snaefell mountain course.
- 1954–1959 FIM World Championship event for motorcycles not exceeding 350 cc engine capacity and held on the Clypse Course.
- 1960–1976 FIM World Championship event for motorcycles not exceeding 350 cc engine capacity and held on the Mountain Course.
- 1977–1994 for motorcycles not exceeding 250 cc engine capacity and held on the Mountain Course.
- 1995 onwards for motorcycles not exceeding 600 cc engine capacity and held on the Mountain Course.
The 2015 specifications for entries into the Supersport TT race are:
-
- TT Supersport: (Machines complying with the 2015 FIM Supersport Championship specifications)
-
-
- Over 400 cc up to 600 cc 4 cylinders 4-stroke
- Over 600 cc up to 675 cc 3 cylinders 4-stroke
- Over 600 cc up to 750 cc 2 cylinders 4-stroke
-
Minimum Weight 161 kg[23]
Superstock TT [edit]
The 2015 specifications for entries for the Superstock TT, an event for production based motorcycles racing with treaded road tyres, are based on the FIM Superstock Championship specifications, as follows:
- Superstock TT: (Machines complying with the 2012 FIM Superstock Championship specifications)
- Over 750 cc up to 1000 cc 4 cylinders 4-stroke
- Over 750 cc up to 1000 cc 3 cylinders 4-stroke
- Over 850 cc up to 1200 cc 2 cylinders 4-stroke
Minimum (Dry) Weight 170 kg[24]
Lightweight TT [edit]

The 1922 event was the first time the Lightweight TT race took place, won by a motorcycle-journalist Geoff S. Davison, riding a Levis at an average speed of 49.89 mph (80.29 km/h) for seven laps of the Snaefell Mountain Course. In the changes following the loss of FIM World Championship status after the 1976 event, the Lightweight TT event was dropped with the 250 cc machines running for the Junior TT in place of the now defunct 350 cc formula. The Lightweight TT returned in 1995 before being split into two distinct events from 1999, dropping from the schedule again after 2003. As with the Ultra-Lightweight TT Race, it was reintroduced 2008–2009 when held on the Billown short road circuit; and then dropped again from the race schedule on cost grounds.
-
- 1924–1948 For motorcycles not exceeding 250 cc engine capacity.
- 1949–1953 FIM World Championship event for motorcycles not exceeding 250 cc engine capacity, held on the Snaefell mountain course.
- 1954–1959 FIM World Championship event for motorcycles not exceeding 250 cc engine capacity, held on the Clypse Course.
- 1960–1976 FIM World Championship event for motorcycles not exceeding 250 cc engine capacity, held on the Mountain Course.
- 1977–1994 event not run (250 cc formula run as Junior TT).
- 1995–1998 for 2-stroke motorcycles not exceeding 250 cc engine capacity, and 4-stroke motorcycles not exceeding 400 cc, held on the Mountain Course.
- 1999–2003 Lightweight 400 TT for 4-stroke motorcycles not exceeding 400 cc engine capacity, held on the Mountain Course.
- 1999–2002 Lightweight 250 TT for 2-stroke motorcycles not exceeding 250 cc engine capacity, held on the Mountain Course (the category running within Junior TT in 2003).
- 2008–2009 for motorcycles not exceeding 250 cc engine capacity, held on the Billown Circuit.
- 2012– The event was re-introduced from the 2012 event for water-cooled four-stroke twin cylinder not exceeding an engine capacity of 650 cc and complying with the ACU Standing Regulations.[25]
The 2019 specifications for entries into the Lightweight TT race are:
-
- Machines must comply with general technical rules as per ACU Standing Regulations and 2019 Isle of Man TT race regulations.
- Any four-stroke twin cylinder motorcycle originally sold for road use with a water-cooled engine of up to 650 cc engine capacity.
- Eligible machines must be from models homologated for UK road use 2009 or later.
- Machines must comply with general technical rules as per ACU Standing Regulations and 2019 Isle of Man TT race regulations.
Mininium weight for the Lightweight TT class is 161 kilograms (355 lb).[26]
Sidecar TT [edit]

Sidecar TT race competitors line up to start the race
The 1923 TT was the first time the Sidecar TT race was run, over three laps (113 mi or 182 km) of the Mountain Course and was won by Freddie Dixon and passenger Walter Denny with a Douglas and special banking-sidecar at an average race speed of 53.15 mph (85.54 km/h). For the 1926 event the Sidecar and Ultra-Lightweight TT classes were dropped due to lack of entries.
The Sidecar race was re-introduced from the 1954 event for Sidecars not exceeding 500 cc engine capacity, run on the Clypse Course. A non-championship 750 cc class for sidecars was introduced at the 1968 event. For the 1976 event the race was held over two-legs. From 1975, the previous 500 cc and 750 cc classes for Sidecars were replaced by a 1000 cc engine capacity class.
The new FIM Formula 2 class for Sidecars was introduced for the 1990 Isle of Man TT.
- 1954–1959 FIM World Championship Event for Side-Cars not exceeding 500 cc engine capacity. Race held on the Clypse Course.
- 1960–1976 FIM World Championship Event held on Mountain Course.
- 1968–1974 Non-Championship event for Sidecars not exceeding 750 cc.
- 1975–1989 Sidecars not exceeding 1000 cc engine capacity.
- 1990– FIM Formula 2 Sidecar race for two-stroke engines not exceeding 350 cc or four-stroke engines not exceeding 600 cc.
The 2015 specifications for entries into the Sidecar TT race are:
- Machines must comply with general technical rules as per ACU Standing Regulations and 2015 Isle of Man TT regulations.
- Engine Types
- 501 – 600 cc, 4 stroke, 4 cylinder, Production based motorcycle engines.
- Engine Types
Senior TT [edit]

For the 1911 Isle of Man TT, the first TT event using the Snaefell Mountain Course or Mountain Course, two separate races were introduced. The first event was a four lap Junior TT race and a separate Senior TT race for 500 cc single-cylinder and 585 cc twin-cylinder motorcycles, over five laps of the new 37.5-mile (60.4 km) Snaefell Mountain Course. The new technical challenges of the Mountain Course forced changes on entrants and motorcycle manufacturers alike. The American Indian motorcycle factory fitted a two-speed gearbox and chain-drive. This proved to be the winning combination when Oliver Godfrey won the 1911 Senior TT race riding an Indian at an average speed of 47.63 mph (76.65 km/h). Fitted with a six-speed belt drive[27] Charlie Collier riding a Matchless motorcycle finished second in the 1911 Senior TT race and was later disqualified for illegal refuelling. During an early morning practice session for the 1911 Isle of Man TT races, Victor Surridge died after crashing his Rudge motorcycle at Glen Helen, the first death of a competitor on the Snaefell Mountain Course and the first death in the Isle of Man of a person in an automotive accident.[28]
-
- 1911 For single cylinder motorcycles not exceeding 500 cc engine capacity and 585 cc twin cylinder motorcycles.
- 1912–1939 For motorcycles not exceeding 500 cc engine capacity.
- 1947–1948 For motorcycles not exceeding 500 cc engine capacity and a ban on engine supercharging.
- 1949–1976 FIM World Championship event for motorcycles not exceeding 500 cc engine capacity.
- 1977–1984 for motorcycles not exceeding 500 cc engine capacity.
- 1985–2004 for motorcycles complying with ACU TT Formula 1 rules not exceeding 1,010 cc engine capacity.
- 2004 onwards for motorcycles complying with ACU/FIM Superbike rules not exceeding 1,000 cc engine capacity.
The 2015 specifications for entries into the Senior TT race are:
- TT Superbike: (Machines complying with the 2015 FIM Superbike Championship specifications)[29]
- Over 750 cc up to 1000 cc 4 cylinders 4-stroke
- Over 750 cc up to 1000 cc 3 cylinders 4-stroke
- Over 850 cc up to 1200 cc 2 cylinders 4-stroke
-
- Supersport Junior TT (without limitation of tyre choice)
- TT Superstock (without limitation of tyre choice)
- Other machines admitted at the discretion of the Organisers.
- Supersport Junior TT (without limitation of tyre choice)
TT Zero [edit]
Starting from the 2010 races, the TT Zero event over one lap (37.73 mi or 60.72 km) of the Snaefell Mountain Course replaced the TTXGP. The TT Zero event as an officially sanctioned TT race is for racing motorcycles where "The technical concept is for motorcycles (two wheeled) to be powered without the use of carbon based fuels and have zero toxic/noxious emissions".[30] The Isle of Man Government offered a prize of £10,000 for the first entrant to exceed the prestigious 100 mph (160 km/h) (22 minutes and 38.388 seconds) average speed around the Mountain Course. This was achieved by Michael Rutter of team MotoCzysz in the 2012 race,[31] and has been exceeded every year since.
Discontinued race classes [edit]
Ultra-Lightweight TT [edit]
1924 was the first time the Ultra-Lightweight TT race took place for motorcycles not exceeding 175 cc engine capacity. It was won by Jock Porter, riding a New Gerrard motorcycle at an average speed of 51.21 mph (82.41 km/h) over three laps of the Snaefell mountain course. The Ultra-Lightweight class was re-introduced in 1951 for motorcycles not exceeding 125 cc until discontinued in 1974, and then re-introduced for 1989, again for two-stroke 125 cc motorcycles, until dropped again due to lack of entries after 2004. The event was reintroduced 2008–2009 held on the four-mile Billown Circuit and then dropped from the race schedule on cost grounds for the 2010 races.
-
- 1924–1925 For motorcycles not exceeding 175 cc engine capacity.
- 1951–1953 FIM World Championship event for motorcycles not exceeding 125 cc engine capacity, held on the Snaefell mountain course.
- 1954–1959 FIM World Championship event for motorcycles not exceeding 125 cc engine capacity, held on the Clypse Course.
- 1960–1974 FIM World Championship event for motorcycles not exceeding 125 cc engine capacity, held on the Mountain Course.
- 1989–2004 for motorcycles not exceeding 125 cc engine capacity, held on the Mountain Course.
- 2008–2009 for motorcycles not exceeding 125 cc engine capacity, held on the Billown Circuit.
-
- 50 cc race 1962–1968, an additional World Championship event for Ultra-Lightweight motorcycles not exceeding 50 cc engine capacity, held on the Mountain Course.
Clubman TT and Production TT [edit]
The Clubman races with Lightweight, Junior and Senior classes were held for production motorcycles from 1947 until 1956.[32] A Senior 1000 cc class provided an opportunity for Vincent motorcycles.[33] The riders were little-known, but as the stars were barred from entering the class, it provided a stepping-stone for future-stars but resulted in less spectator-interest. The series became dominated by one model – the BSA Gold Star,[34] [35] [36] and with little competition from other manufacturers, was discontinued. When previewing the impending re-introduction of a specification-controlled, roadster-based class in March 1967, David Dixon wrote: "lack of inter-make rivalry probably put the final nail in the coffin".[34]
Writing in UK monthly magazine Motor Cyclist Illustrated, racing journalist Ray Knight, who had achieved a lap speed of nearly 88 mph on a Triumph Tiger 100 roadster-based racing motorcycle in the Manx Grand Prix,[37] [38] [39] commented in early 1965 that the ACU had refused a request from manufacturers to run a production TT race, which he thought was a missed opportunity, particularly considering the dwindling support for the 500 cc race.[40]
A Production TT for roadster-based motorcycles having classes for maximum engine capacities of 250 cc, 500 cc and 750 cc was introduced from 1967 until 1976 when the class was discontinued.
The Production TT was reintroduced for the 1984 races in three classes, reduced to two classes on safety grounds for the 1990 races. For the 2005 races the Superstock class replaced the previous 1000 cc and 600 cc Production TT classes that had been part of the race schedule since 1989.
Practice sessions [edit]

2013 TT start of the Newcomers Speed Control Lap with John McGuinness (left) and Bruce Anstey (right)
The format of the Isle of Man TT is one week of practice/qualifying followed by one week of racing. Historically, there was an early morning practice session from 05:00–07:30 am. This was discontinued for the 2004 Isle of Man TT races.
During an early morning practice session for the 1927 Isle of Man TT races, Archie Birkin, brother of Tim Birkin of the Bentley Boys fame, crashed fatally at Rhencullen after swerving to avoid a collision with a Fish Van being driven on open roads.[41] From 1928 onwards, practice sessions for the Isle of Man TT Races and Manx Grand Prix were held on closed public roads.[42] Evening practice sessions were introduced for the 1937 Isle of Man TT races and continue to this day.[43]
The Thursday afternoon practice session were discontinued from the Centenary 2007 Isle of Man TT races and replaced with an evening practice session. For the 2015 Isle of Man TT races, a Saturday evening untimed practice session from 18:00–21:30 was added to the schedule. For the 2020 Isle of Man TT races, a revised practice schedule is introduced with the first practice session moved from Saturday evening to Sunday afternoon.[44] The first practice sessions provide controlled laps for newcomers. Competitors are escorted for one lap of the Isle of Man TT Mountain Course by the Travelling Marshals at a steady pace and accompanied by experienced Isle of Man TT and/or Manx Grand Prix competitors.
Current practice session schedule [edit]

Start of a practice session
The section of the primary A18 Snaefell Mountain Road from Ramsey Hairpin to the Creg-ny-Baa to close at 16:45 pm for the practice periods (from 17:00 hours from the Bungalow), 1 hour and 15 minutes before the rest of the TT Course at 18:00 pm.[45]
The schedule for the first Sunday untimed session on Sunday 30 May 2021:
- 13:30 Newcomers Speed Control Lap
- 13:50 Superbike TT / Superstock TT / Supersport TT
- 15:30 Lightweight TT / Supersport TT / Newcomers (all solo classes)
- 16:30 Sidecar TT
Practice week sessions [edit]
The main practice and timed practice sessions are usually held on Monday-Friday of the next week. The public roads forming the Isle of Man TT Mountain Course will be closed in for the 2021 Isle of Man TT races for the Solo and Sidecar classes.
Schedule for the four-day evening timed session Monday-Thursday of practice week:
Monday 31 May to Thursday 3 June 2020:
- 18:20 – 19:55 Solo Motor-Cycles timed practice session.
- 20:00 – 20:50 Sidecar timed practice session.
For Friday 4 June 2021 an afternoon practice session with a provisional evening practice session:
- 13:00 – 14:55 Solo Motor-Cycles timed practice session.
- 15:05 Sidecar timed practice session.
In the event of inclement weather either delaying or leading to the cancellation of one or more timed practice sessions, a reserve morning session could be held with the public roads closed 06:00 – 07:30 on the Isle of Man TT Mountain Course. Further untimed practice sessions are held during race week after the racing has been completed for selected race classes.
The 2020 event was cancelled due to the COVID-19 pandemic.[46]
TT course official vehicles [edit]
After the completion of a practice or race period, an official course vehicle displaying the notice Roads Open proceeds around the Mountain Course, passing each point opening the roads including side-access junctions to public use. On the Snaefell mountain road section from Ramsey to Douglas, the official vehicle displays the notice Roads Open One Way.
Travelling Marshals [edit]
Originally introduced in 1935, there are eight machines positioned around the course to provide a rapid response to any incidents. Selected riders have previous race experience and are first-aid trained, with machines carrying medical equipment that can assist in managing a casualty. They also have other duties such as course inspection, observation of machines on the course for visible faults, and review and report any course incidents.[47]
Crossing places during practice and races [edit]
The 1982 Road Racing Act (Isle of Man) and the supplementary TT Road Races Orders allow vehicles and pedestrians to cross the Snaefell Mountain Course at certain points between scheduled race periods under the supervision of a police officer. Several permanent pedestrian overbridges have been erected. These points include:
In Douglas [edit]
- A2 St Ninian's Crossroads with the A22 Ballaquayle Road and the A22 Ballanard Road
- A2 junction at Bray Hill with the Tromode Road and Stoney Road
- A1 Peel Road between Braddan Bridge (Jubilee Oak) and the Quarterbridge
- A2 Governor's Road, Onchan, the A2 Glencrutchery Road and Victoria Road at Governor's Bridge
- A2 Glencrutchery Road between Second & Third Avenues and Victoria Road
- A18 Bemahague Road at Bedstead Corner, Onchan
-

Pedestrian overbridge at Glencrutchery Road, Douglas, close to start/finish and TT Grandstand
-

Pedestrian overbridge at Bedstead Corner, Douglas, with Hailwood Avenue junction to right
Elsewhere [edit]
- A1 Douglas to Peel road with the A23 Eyreton Road and the B36 Old Church Road, Crosby
- A3 Castletown to Ramsey road junction with B10 Sartfield Road and the Ballaleigh Road at Barregarrow Crossroads, Michael
- A3 junction with A10 Station Road and C37 Ballaugh Glen Road at Ballaugh Bridge
- A3 junction with A14 Sandygate Road and A14 Tholt-y-Will Glen Road at Sulby Crossroads
- A2 Albert Square and Princes Road, Ramsey at the junction with A18 Snaefell Mountain Road, close to May Hill
-

Pedestrian overbridge exiting Ramsey town centre, looking south-east towards May Hill
TT Course access road [edit]

Part of the access road passing under the A1 Peel Road
The TT Access Road runs parallel to a section of the A1 Peel Road, which is part of the Snaefell Mountain Course, and operates during practice and race periods to enable vehicles to pass from inside of the race course to the outside. It runs along a section of former railway line on the historic Douglas to Peel route, from the junction of the A5 New Castletown Road at the Quarter Bridge, passing under the course at Braddan Bridge, to an exit at Braddan School Road in Douglas outskirts, near the former Braddan Railway Halt and the A23/Ballafletcher Road junction. The access road is a narrow, single-track width with passing places and is restricted to cars and light vans below a weight limit of 3,500 kilograms (3.4 long tons; 3.9 short tons). When used for vehicular traffic, pedestrian access is prohibited, but at other times it is part of a system of nature trails.[48] [49]
Description [edit]
The Oxford Companion to World Sports and Games notes:
The oldest motor-cycle racing circuit still in use is the Snaefell Mountain Course over which the Isle of Man Tourist Trophy races are run. Starting at the town of Douglas on the south-east coast, the course takes a wide sweep to the west and north to enter the town of Ramsey on the north-east coast and thence return to the starting point, each lap measuring 37 3⁄4 miles (60.7 km) and taking in over 200 bends while climbing from sea level to an altitude of over 1,300 ft (396 m). This circuit is the epitome of the natural road course, all the roads used being ordinary public highways closed for the racing and practice sessions.[50]
During race week, the TT races create a carnival atmosphere with picnicking spectators flanking vantage points on the circuit similar to other community festivals in another form of cycle racing – the Tour de Yorkshire and Le Tour de France.
Safety [edit]
Between 1907 and 2019 there have been 151 fatalities during official practices or races on the Snaefell Mountain Course, and 260 total fatalities (this number includes the riders killed during the Manx Grand Prix, and Clubman TT race series of the late 1940s/1950s).[8] [51] [52] In 2016, 5 riders died on the course during official practices or races, bringing the total number of fatalities to 252.[53] [54] [9] [55] There were six fatalities among competitors in the 1970 Isle of Man TT, making it the deadliest year in the history of the event.[56] [57]
2018 Course Car incident [edit]

Sidecars returning to Paddock past Sarah's Cottage in reverse direction to a normal race, after a Red Flag race stoppage caused by a competitor crash during 2009
On 30 May 2018 an experienced TT rider, Steve Mercer,[58] [59] was seriously injured during a head-on collision with an official Course Car at Ballacrye. The car, being driven at high speed,[60] [61] was conveying police officers to officiate at the scene of a fatality involving Dan Kneen. Mercer was unconscious for five days and hospitalised for five months due to multiple injuries. He was one of seven riders who had been halted on the course and turned back by marshals, being instructed to proceed back to the TT Grandstand area in the reverse-direction after the red flag stoppage.[62] [63] This caused organisers to immediately change their protocols, requiring that returning riders must be controlled by motorcycle-mounted travelling marshals to the front and rear.[64] [65] An independent inquiry to probe the circumstances was arranged by ACU Events, the event organisers.[66]
The Auto-Cycle Union and the Isle of Man Department for Enterprise, together with report author, lawyer Rob Jones, a former chief executive of the Motor Sports Association, all refused to release the report as it was confidential and privately owned by the ACU.[61] [63] [67] [68]
The ACU admitted liability for the accident, but instructed that any legal claim for compensation by Mercer must be filed in the Isle of Man. The ACU stated that Mercer was receiving financial assistance through its "extensive insurance arrangements".[59] [69] [70]
In 2019 it was revealed that the same driver had quit after criticism that he exceeded a newly introduced speed limit recorded by a GPS Tracking device when he drove to attend a fatality involving Chris Swallow at Ballaugh in August's Senior Classic TT. Gary Thompson MBE, Clerk of the Course and an ACU employee, had been criticised in 2018 for also fulfilling the role of Safety Officer, consequently a new incumbent was in place for 2019.[61] [71] [72]
Cancellations [edit]
World Wars I and II [edit]
From 1915 to 1919, and 1940 to 1946, no TT events took place, due to the outbreak of World Wars I and II.[73] Events continued from 1920 to 1939 and 1947 to 2000.
Since TT 1947, the Isle of Man TT has only been cancelled three times; 2001, 2020 and 2021, all of which were due to viral outbreaks.
2001 cancellation [edit]
The 2001 Isle of Man TT races were cancelled, and did not take place because of the outbreak of foot-and-mouth disease in the UK in the spring and summer of 2001, and the difficulties of disinfecting 40,000 spectators and competitors (and their motorcycles) to ensure the disease was kept off the island.
2020 and 2021 cancellations [edit]
In March 2020, the Isle of Man Government announced the cancellation of the 2020 TT due to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic.[74] The Classic TT was subsequently cancelled in May,[75] and in December 2020, it was announced that 2021's TT races would also not go ahead, due to the continued worldwide spread of the virus.[76] TT 2022 is still expected to go ahead as scheduled.[77]
In 2020, the Isle of Man Government lost an estimated £4.8 million of its annual projected revenue due to the cancellation of the TT races.[78]
Total overall race winners [edit]
[79]
| Rider | Wins |
|---|---|
| Joey Dunlop | 26 |
| John McGuinness | 23 |
| Michael Dunlop | 19 |
| Dave Molyneux | 17 |
| Ian Hutchinson | 16 |
| Mike Hailwood | 14 |
| Bruce Anstey | 12 |
| Steve Hislop, Phillip McCallen | 11 |
| Giacomo Agostini, Robert Fisher, Ian Lougher, Stanley Woods | 10 |
| Mick Boddice, Dave Saville, David Jefferies, Siegfried Schauzu | 9 |
| Ben Birchall, Tom Birchall, Jim Moodie, Chas Mortimer, Phil Read, Dan Sayle, Charlie Williams | 8 |
| Mick Grant, Wolfgang Kalauch, Tony Rutter | 7 |
| Chas Birks, Geoff Duke, Jimmie Guthrie, Rick Long, Jim Redman, Michael Rutter, John Surtees | 6 |
| Alec Bennett, Nick Crowe, Robert Dunlop, Brian Reid, Carlo Ubbiali, Peter Hickman | 5 |
| Klaus Enders, Freddie Frith, Wal Handley, Trevor Ireson, Benga Johansson, Dave Leach, Chris Palmer, Ray Pickrell, Tarquinio Provini, Horst Schneider, Barry Smith, Bill Smith, Jock Taylor, John Williams, | 4 |
| Ray Amm, Adrian Archibald, Graeme Crosby, Harold Daniell, Max Deubel, Ralf Engelhardt, Ryan Farquhar, Patrick Farrance, Carl Fogarty, Alex George, Tom Herron, Darren Hope, Emil Hörner, Alan Jackson, Tony Jefferies, Geoff Johnson, Klaus Klaffenböck, Rob McElnea, Bob McIntyre, Phil Mellor, Dave Morris, Clive Pollington, Walter Schneider, Ian Simpson, Rolf Steinhausen, Hans Strauss, Luigi Taveri, Don Williams, Barry Woodland Dean Harrison | 3 |
| Fergus Anderson, Hugh Anderson, Manliff Barrington, Artie Bell, Geoff Bell, Lowry Burton, Kel Carruthers, Bernard Codd, Charlie Collier, Keith Cornbill, Mark Cox, Steve Cull, Pat Cushnahan, Howard R Davies, Freddie Dixon, Charlie Dodson, Cameron Donald, Iain Duffus, Karl Ellison, Bob Foster, Dick Greasley, Manfred Grunwald, Hermann Hahn, Craig Hallam, Shaun Harris, John Hartle, Pete Hill, Fritz Hillebrand, Mac Hobson, Gary Hocking, John Holden, Josef Huber, Tim Hunt, Bill Ivy, Gary Johnson, Alistair King, Con Law, Eddie Laycock, Ivan Lintin, Bill Lomas, Nick Long, Graeme McGregor, Trevor Nation, Gary Padgett, Steve Plater, Jock Porter, Nick Roche, Cecil Sandford, Dave Saville, Tom Sheard, Edwin Twemlow, Malcolm Uphill, Dave Wells, Eric Williams, Paul Williams, Andrew Winkle, Michael Wynn, | 2 |
| Steve Abbott, Dario Ambrosini, Frank A Applebee, Ivor Arber, Reg Armstrong, Kenny Arthur, Stewart Atkinson, Georg Auerbacher, Mike Aylott, Mark Baldwin, Rob Barber, W. Harry Bashall, Ian Bell, Phillip Biggs, Eric Bliss, Dieter Braun, Eric Briggs, Norman Brown, Ralph Bryans, Jimmy Buchan, Trevor Burgess, Roger Burnett, Mick Burns, Florian Camathias, Maurice Cann, Neil Carpenter, Phil Carpenter, Phil Carter, Harold Clark, Rod Coleman, Harry A Collier, Stuart Collins, Syd Crabtree, Dave Croxford, J.D. Daniels, Leo Davenport, Geoff Davison, Tommy de la Hay, Ernst Degner, Walter Denny, George Douglas, Eddie Dow, Percy Evans, Helmut Fath, Jack Findlay, John Flaxman, Frank Fletcher, Rem Fowler, John Gibbard, Sid Gleave, Oliver Godfrey, Les Graham, Stuart Graham, Werner Haas, Dave Hallam, Roy Hanks, Colin Hardman, Bernard Hargreaves, Conrad Harrison, Ron Haslam, Ronnie Hazlehurst, Chris Heath, Alfred Herzig, Freddie Hicks, James Hillier, Robert Holden, Rupert Hollaus, Colin Hopper, Ken Horstman, Clive Horton, Eric Housley, Dennis Ireland, Mitsuo Itoh, Brian Jackson, Nick Jefferies, Doug Jewell, Lee Johnston, C. W. Johnston, Ken Kavanagh, Bob Keeler, Neil Kelly, Basil Keys, John Kidson, Ewald Kluge, Ray Knight, David Lashmar, Monty V. Lockwood, Frank Longman, Heinz Luthringshauser, Jack Marshall, Keith Martin, Hugh Mason, Cromie McCandless, Georg Meier, Ted Mellors, Mark Miller, Derek Minter, Brian Morrison, Les Nutt, George O'Dell, Eric Oliver, Mat Oxley, Len Parker, Philip Parker, Denis Parkinson, Graham Penny, Alex Phillip, Derek Powell, Cyril Pullin, Brian Purslow, Richard Quayle, Johnny Rea, Harry Reed, Tim Reeves, Brett Richmond, Tommy Robb, John Robinson, Mike Rogers, Nigel Rollason, Dave Roper, Gordon Russell, Fritz Scheidegger, Martyn Sharpe, Dave Simmonds, Bill Simpson, Jimmie Simpson, Cyril Taft, Omobono Tenni, Steve Tonkin, George Tucker, Kenneth Twemlow, Henry Tyrell-Smith, Chris Vincent, Terry Vinicombe, Graham Walker, Frank Whiteway, Cyril Williams, Peter Williams, Alfred Wohlgemuth, Tim Wood, Tommy Wood, Stan Woods | 1 |
FIM Motorcycle Grand Prix World Championship Rounds (1949–1976) [edit]
 | |
| Grand Prix motorcycle racing | |
|---|---|
| Venue | Snaefell Mountain Course |
| First race | 1949 |
| Last race | 1976 |
| Most wins (rider) | Mike Hailwood (12) |
| Most wins (manufacturer) | MV Agusta (33) |
The Isle of Man TT was part of the FIM Motorcycle Grand Prix World Championship (now MotoGP) between 1949 and 1976. During this period the Isle of Man TT Races counted as the United Kingdom round including the Sidecar TT, 50 cc Ultra-Lightweight TT, 125 cc Lightweight TT, 250 cc Lightweight TT, 350 cc Junior TT and 500 cc Senior TT races counted towards the FIM Motor-Cycle Grand Prix World Championship. After the 1972 races, multiple world champion and dominant motorcycle racer of his time Giacomo Agostini announced he would never race again at the Isle of Man, declaring it too dangerous for international competition and that it was outrageous that such a race should ever be part of a scenario professional riders were forced into; at this point the Isle of Man TT was not suited to the growing professionalism and business aspects of Grand Prix motorcycle racing. More and more riders joined his boycott, and after 1976 the race was stricken from the championship and replaced by the British Grand Prix.
Multiple winners (riders) [edit]
| # Wins | Rider | Wins | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Years won | ||
| 12 | | 500 cc | 1961, 1963, 1964, 1965, 1966, 1967 |
| 350 cc | 1962, 1967 | ||
| 250 cc | 1961, 1966, 1967 | ||
| 125 cc | 1961 | ||
| 10 | | 500 cc | 1968, 1969, 1970, 1971, 1972 |
| 350 cc | 1966, 1968, 1969, 1970, 1972 | ||
| 6 | | 500 cc | 1956, 1958, 1959, 1960 |
| 350 cc | 1958, 1959 | ||
| | 350 cc | 1963, 1964, 1965 | |
| 250 cc | 1963, 1964, 1965 | ||
| | 350 cc | 1961 | |
| 250 cc | 1971, 1972 | ||
| 125 cc | 1965, 1967, 1968 | ||
| 5 | | 500 cc | 1950, 1951, 1955 |
| 350 cc | 1951, 1952 | ||
| | 250 cc | 1956 | |
| 125 cc | 1955, 1956, 1958, 1960 | ||
| 4 | | 250 cc | 1958, 1959 |
| 125 cc | 1957, 1959 | ||
| | 350 cc | 1976 | |
| 250 cc | 1975 | ||
| 125 cc | 1971, 1972 | ||
| 3 | | 500 cc | 1953, 1954 |
| 350 cc | 1953 | ||
| | 125 cc | 1962, 1964 | |
| 50 cc | 1965 | ||
| | 350 cc | 1975 | |
| 250 cc | 1973, 1974 | ||
| 2 | | 250 cc | 1952, 1953 |
| | 350 cc | 1955 | |
| 250 cc | 1955 | ||
| | 250 cc | 1957 | |
| 125 cc | 1952 | ||
| | 500 cc | 1957 | |
| 350 cc | 1957 | ||
| | 500 cc | 1962 | |
| 250 cc | 1960 | ||
| | 125 cc | 1963 | |
| 50 cc | 1964 | ||
| | 250 cc | 1968 | |
| 125 cc | 1966 | ||
| | 250 cc | 1969, 1970 | |
| | 350 cc | 1973, 1974 | |
| | 500 cc | 1976 | |
| 250 cc | 1976 | ||
Multiple winners (manufacturers) [edit]
| # Wins | Manufacturer | Wins | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Years won | ||
| 33 | | 500 cc | 1956, 1958, 1959, 1960, 1962, 1963, 1964, 1965, 1968, 1969, 1970, 1971, 1972 |
| 350 cc | 1958, 1959, 1960, 1962, 1966, 1968, 1969, 1970, 1972 | ||
| 250 cc | 1956, 1958, 1959, 1960 | ||
| 125 cc | 1952, 1953, 1955, 1956, 1958, 1959, 1960 | ||
| 21 | | 500 cc | 1974, 1976 |
| 350 cc | 1973, 1974, 1975, 1976 | ||
| 250 cc | 1968, 1970, 1971, 1972, 1973, 1974, 1975, 1976 | ||
| 125 cc | 1965, 1966, 1967, 1968, 1971, 1972, 1973 | ||
| 18 | | 500 cc | 1966, 1967 |
| 350 cc | 1963, 1964, 1965, 1967 | ||
| 250 cc | 1961, 1962, 1963, 1964, 1965, 1966, 1967 | ||
| 125 cc | 1961, 1962, 1964 | ||
| 50 cc | 1965, 1966 | ||
| 12 | | 500 cc | 1949, 1950, 1951, 1952, 1953, 1954, 1961 |
| 350 cc | 1950, 1951, 1952, 1953, 1961 | ||
| 7 | | 350 cc | 1955, 1956 |
| 250 cc | 1949, 1951, 1952, 1953, 1955 | ||
| | 500 cc | 1973 | |
| 125 cc | 1963, 1970 | ||
| 50 cc | 1962, 1963, 1964, 1967 | ||
| 3 | | 250 cc | 1957 |
| 125 cc | 1951, 1957 | ||
| | 500 cc | 1955, 1957 | |
| 350 cc | 1957 | ||
| 2 | | 250 cc | 1954 |
| 125 cc | 1954 | ||
| | 250 cc | 1950, 1969 | |
| | 500 cc | 1975 | |
| 125 cc | 1969 | ||
By year [edit]
| Year | 50 cc (Ultra-Lightweight TT) | 125 cc (Lightweight TT) | 250 cc (Lightweight TT) | 350 cc (Junior TT) | 500 cc (Senior TT) | Report | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rider | Manufacturer | Rider | Manufacturer | Rider | Manufacturer | Rider | Manufacturer | Rider | Manufacturer | ||
| 1976 | | Yamaha | | Yamaha | | Yamaha | Report | ||||
| 1975 | | Yamaha | | Yamaha | | Kawasaki | Report | ||||
| 1974 | | Yamaha | | Yamaha | | Yamaha | Report | ||||
| 1973 | | Yamaha | | Yamaha | | Yamaha | | Suzuki | Report | ||
| 1972 | | Yamaha | | Yamaha | | MV Agusta | | MV Agusta | Report | ||
| 1971 | | Yamaha | | Yamaha | | Yamsel | | MV Agusta | Report | ||
| 1970 | | Suzuki | | Yamaha | | MV Agusta | | MV Agusta | Report | ||
| 1969 | | Kawasaki | | Benelli | | MV Agusta | | MV Agusta | Report | ||
| 1968 | | Derbi | | Yamaha | | Yamaha | | MV Agusta | | MV Agusta | Report |
| 1967 | | Suzuki | | Yamaha | | Honda | | Honda | | Honda | Report |
| 1966 | | Honda | | Yamaha | | Honda | | MV Agusta | | Honda | Report |
| 1965 | | Honda | | Yamaha | | Honda | | Honda | | MV Agusta | Report |
| 1964 | | Suzuki | | Honda | | Honda | | Honda | | MV Agusta | Report |
| 1963 | | Suzuki | | Suzuki | | Honda | | Honda | | MV Agusta | Report |
| 1962 | | Suzuki | | Honda | | Honda | | MV Agusta | | MV Agusta | Report |
| 1961 | | Honda | | Honda | | Norton | | Norton | Report | ||
| 1960 | | MV Agusta | | MV Agusta | | MV Agusta | | MV Agusta | Report | ||
| 1959 | | MV Agusta | | MV Agusta | | MV Agusta | | MV Agusta | Report | ||
| 1958 | | MV Agusta | | MV Agusta | | MV Agusta | | MV Agusta | Report | ||
| 1957 | | Mondial | | Mondial | | Gilera | | Gilera | Report | ||
| 1956 | | MV Agusta | | MV Agusta | | Moto Guzzi | | MV Agusta | Report | ||
| 1955 | | MV Agusta | | Moto Guzzi | | Moto Guzzi | | Gilera | Report | ||
| 1954 | | NSU | | NSU | | AJS | | Norton | Report | ||
| 1953 | | MV Agusta | | Moto Guzzi | | Norton | | Norton | Report | ||
| 1952 | | MV Agusta | | Moto Guzzi | | Norton | | Norton | Report | ||
| 1951 | | Mondial | | Moto Guzzi | | Norton | | Norton | Report | ||
| 1950 | | Benelli | | Norton | | Norton | Report | ||||
| 1949 | | Moto Guzzi | | Velocette | | Norton | Report | ||||
Current lap records [edit]
| Category | Rider(s) | Machine | Tyres | Year | Time | Average speed | Source[80] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mph | km/h | |||||||
| Outright (all categories) | Peter Hickman | BMW S1000RR | Dunlop | 2018 | 16:42.778 | 135.452 | 217.989 | [1] |
| Superbike TT | Dean Harrison | Kawasaki | Metzeler | 2018 | 16:50.384 | 134.432 | 216.347 | [81] |
| Supersport TT | Michael Dunlop | Honda CBR600RR | Dunlop | 2018 | 17:31.328 | 129.197 | 207.922 | [82] |
| Lightweight TT | Michael Dunlop | Paton | 2018 | 18:26.543 | 122.750 | 197.547 | [83] | |
| Ultra-Lightweight TT | Chris Palmer | Honda RS125 | 2004 | 20:20.87 | 110.52 | 177.86 | ||
| Senior TT | Peter Hickman | BMW S1000RR | Dunlop | 2018 | 16:42.778 | 135.452 | 217.989 | [84] |
| Superstock TT | Peter Hickman | BMW S1000RR | Dunlop | 2018 | 16:50.601 | 134.403 | 216.301 | [85] |
| TT Zero | Michael Rutter | Mugen Shinden | 2019 | 18:34:172 | 121.91 | 196.20 | [86] | |
| Sidecar TT | Ben Birchall and Tom Birchall | Honda CBR Sidecar | Avon | 2018 | 18:59.018 | 119.250 | 191.914 | [87] |
Current race records [edit]
| Category | Laps | Rider(s) | Machine | Tyres | Year | Race time | Average speed | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mph | km/h | |||||||
| Superbike TT | 6 | Michael Dunlop | BMW S1000RR | Dunlop | 2018 | 01:44:13.398 | 130.324 | 209.736[81] |
| Supersport TT | 4 | Dean Harrison | Kawasaki ZX6-R | Metzeler | 2018 | 01:11:28.059 | 126.703 | 203.909[88] |
| Lightweight TT | 4 | Michael Dunlop | Paton 650 | Metzeler | 2018 | 01:15:05.032 | 120.601 | 194.088[83] |
| Lightweight TT | 3 | Ivan Lintin | Kawasaki ER650 | Metzeler | 2015 | 57:06.070 | 118.936 | 191.409[89] |
| Senior TT | 6 | Peter Hickman | BMW S1000RR | 2018 | 01:43:08.065 | 131.700 | 211.951[84] | |
| Senior TT | 4 | John McGuinness | Honda CBR1000RR | Dunlop | 2015 | 01:09:23.903 | 130.481 | 209.989 |
| Superstock TT | 4 | Peter Hickman | BMW S1000RR | Dunlop | 2018 | 01:08:49.976 | 131.553 | 211.714[85] |
| TT Zero | 1 | Michael Rutter | Mugen Shinden | 2019 | 18:34.172 | 121.91 | 196.20[86] | |
| Sidecar TT | 3 | Ben Birchall and Tom Birchall | Honda CBR Sidecar | Avon | 2018 | 57:25.040 | 118.281 | 190.355[87] |
Race awards [edit]
Race winner trophies [edit]
| Race | Trophy | Rider(s) | Machine | Tyres | Year | Average speed | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mph | km/h | ||||||
| Senior TT | Senior Tourist Trophy1 | Michael Dunlop | Suzuki GSX-R1000 | Dunlop | 2017 | 130.456 | 209.949 |
| TT Superbike | TT Superbike Trophy | Michael Dunlop | BMW S1000RR | Dunlop | 2018 | 130.324 | 209.736[81] |
| TT Superstock | John Hartle Trophy | Peter Hickman | BMW S1000RR | Dunlop | 2018 | 131.553 | 211.714[85] |
| TT Supersport Race 1 | Junior Tourist Trophy | Michael Dunlop | Honda CBR600RR | Dunlop | 2018 | 126.027 | 202.821[82] |
| TT Supersport Race 2 | Classic TT Trophy | Ian Hutchinson | Yamaha YZF-R6 | Metzeler | 2016 | 125.905 | 202.624[90] |
| TT Lightweight | Lightweight TT Trophy | Michael Rutter | Paton S1 | Dunlop | 2017 | 118.645 | 190.941 |
| TT Sidecar Race 1 | Fred W. Dixon Trophy | Ben Birchall and Tom Birchall | Honda CBR Sidecar | Avon | 2018 | 117.987 | 189.882[87] |
| TT Sidecar Race 2 | Sidecar TT Trophy | Ben Birchall and Tom Birchall | LCR Honda 600 cc | Avon | 2017 | 115.760 | 186.298 |
- ^1 Marquis de Mouzilly St Mars Trophy.
Fastest lap awards [edit]
| Race | Trophy | Rider(s) | Machine | Year | Average speed | Time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mph | km/h | ||||||
| Overall | Jimmy Simpson Trophy | Michael Dunlop | Suzuki GSX-R1000 | 2017 | 132.903 | 213.887 | 17:02.009 |
| Senior TT | Norman Brown Trophy | Michael Dunlop | Suzuki GSX-R1000 | 2017 | 132.903 | 213.887 | 17:02.009 |
| TT Superbike | John Williams Trophy | Dean Harrison | Kawasaki Ninja ZX-10R | 2018 | 134.432 | 216.347 | 16:50.384[1] |
| TT Superstock | Don Ryder Trophy | Peter Hickman | BMW S1000RR | 2018 | 134.403 | 216.301 | 16:50.601[85] |
| TT Supersport Race | Formula 2 TT Trophy | Peter Hickman | Triumph Daytona 675 | 2017 | 126.848 | 204.142 | 17:50.792 |
| TT Sidecar Race | Jock Taylor Trophy | Ben Birchall and Tom Birchall | LCR Honda 600 Sidecar | 2017 | 117.119 | 188.485 | 19:19.746 |
Special awards [edit]
| Award | Trophy | Rider(s) | Machine | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TT Solo Championship | Joey Dunlop Trophy | Ian Hutchinson | BMW S1000RR Yamaha YZF-R6 | 2016[91] |
| TT Privateer's Champion | TT Privateer's Champion | Daniel Hegarty | Kawasaki Ninja ZX-10R Kawasaki Ninja ZX-6R | 2016[91] |
| Overall Sidecar Championship | RAC Sidecar Trophy | John Holden and Andrew Winkle | LCR Suzuki 600 cc | 2016[92] |
| Sidecar Passenger Championship | Craig Trophy | Andrew Winkle | LCR Suzuki 600 cc | 2016[92] |
| Supersport Championship | TT Supporters' Club Trophy | Ian Hutchinson | Yamaha YZF-R6 | 2016 |
| Sidecar Chassis Championship | Fred Hanks Trophy | John Holden and Andrew Winkle | LCR Suzuki 600 cc | 2016[92] |
| Newcomers Sidecar Driver Championship | Peter Chapman Trophy | Lionel Mansuy | Windle 600 cc | 2015 |
| Newcomers Sidecar Passenger Championship | Dave Wells Trophy | Matty Ramsden | LCR 600 cc | 2015 |
| British competitor British manufacturer | Joe Craig Trophy | Guy Martin | Triumph 675 cc | 2015 |
| Irish (North or South) solo competitor | Martin Finnegan Trophy | Michael Dunlop | BMW S1000RR | 2016[91] [93] |
| Isle of Man solo competitor | Gavin Lee Trophy | Conor Cummins | Honda CBR1000RR | 2016[93] |
| International Team Award – USA | Dwight Mitchell[94] Garett King Stephen John | Kawasaki Ninja ZX-6R Honda CBR 600 | 1999[95] [96] [97] |
Other Special awards [edit]
-
-
- Fastest Newcomer – The Vernon Cooper Trophy
-
-
-
-
-
Rider(s) Machine Year Average speed Time mph km/h Lukas Maurer Kawasaki 1000 cc 2019 123.645 198.987 18:18.529[98]
-
-
-
-
-
- Most Meritorious Female – The Susan Jenness Trophy is awarded yearly by the Executive Committee of the TT Supporters' Club, in recognition of the "most meritorious performance by a female competitor" during the previous TT meeting.[99]
-
-
-
-
-
-
Rider(s) Race Category Year Jenny Tinmouth solo competitor 2010 Fiona Baker-Milligan as passenger, Sidecar 600 cc 2011[100] Debbie Baron as driver, Ireson Kawasaki Sidecar 600 cc 2012[101] Estelle Leblond as driver, Sidecar 600 cc 2013[102] Estelle Leblond as driver, Sidecar 600 cc 2014[103] Fiona Baker-Milligan as passenger, Sidecar 600 cc 2015[104] Maria Costello solo competitor 2016[105] Estelle Leblond & Melanie Farnier Sidecar 600 cc 2017[106] Julie Canipa as passenger, Sidecar 600 cc 2018[107] (undecided) 2019
-
-
-
-
Video games [edit]
There have been numerous videogames based on the Isle of Man TT, the first being the 1995 Sega arcade game Manx TT Super Bike, which was later ported to the Sega Saturn in 1997.[108] Several other games have followed since, including Suzuki TT Superbikes (2005), TT Superbikes: Real Road Racing Championship and TT Superbikes Legends (both 2008), all of which were released exclusively for the PlayStation 2, and developed by Jester Interactive.
Bigben Interactive has since revived the TT game license, releasing TT Isle Of Man: Ride on the Edge in 2018 and TT Isle Of Man: Ride on the Edge 2 in 2020.[109] [110]
In popular culture [edit]
"Riding in the TT Races" is a song written and sung by George Formby in the 1935 film No Limit.
See also [edit]
- List of named corners of the Snaefell Mountain Course
- North West 200
- Outline of motorcycles and motorcycling

Notes [edit]
Citations [edit]
- ^ a b c "Isle of Man TT results: Peter Hickman becomes the world's fastest rider with record-breaking Senior TT victory". Isle of Man TT. Duke Marketing Limited. 2 June 2018. Retrieved 3 June 2018.
Peter Hickman produces an astonishing record final lap to win the Senior TT at the Isle of Man TT to pip race-long leader Dean Harrison in one of the closest races ever seen.
- ^ The Manx Experience. A Souvenir Guide to the Isle of Man. page 66-67 Gordon N.Kniverton 8th edition The Manx Experience (1987) Mannin Publishing Ltd
- ^ Isle of Man Examiner page 2 12 November 1921
- ^ Here Is the News: A Chronicle of the 20th Century, Volume 1 page 78 Gordon N.Kniverton & Terry Cringle Manx Heritage Foundation (1999) The Manx Experience ISBN 9781873120460
- ^ Official Programme – International Auto-Cycle Tourist Trophy 28 May 1907 pages 1–3 The Auto-Cycle Club (1907). Reproduction (2007) Isle of Man Post Office
- ^ Huber, Tim. "Everything You Need To Know About: The Isle of Man TT". RideApart.com.
- ^ 'Motor-Cycle pages 1 & 6 14 June 1972
- ^ a b KEH, ANDREW (7 June 2017). "Take a Lap in the World's Most Dangerous Race". New York Times . Retrieved 26 October 2017.
- ^ a b DeGroot, Nick (5 June 2016). "Two fatalities in a single day rock the 2016 Isle of Man TT". Motorsport.com. Retrieved 7 February 2017.
- ^ "38 Miles of Terror", 09.08.03 – Sports Illustrated
- ^ Isle of Man's Big 3 Race Events : The Spectator Guide. TT (Tourist Trophy), Festival of Motorcycling (incorporating Manx Grand Prix), Southern 100 page 43 Trevor Barret (2014) Lily Publication ISBN 1907945237
- ^ "3 Dead After 2017 Isle of Man TT Crashes: Lambert, Hoek, Bonner". Ultimate Motorcycling. 7 June 2017.
- ^ "Isle of Man Judgments Online". judgments.im.
- ^ "Isle of Man Judgments Online". judgments.im.
- ^ "Coronavirus: Isle of Man cancels TT races amid virus outbreak". BBC News. 16 March 2020.
- ^ "2021 TT Festival: Covid-19 fears force Manx government to cancel event". BBC Sport. 30 November 2020. Retrieved 20 January 2021.
- ^ Island Racer 2004 pp 112–113 Mortons Media Group Ltd. ISBN 9780954244224
- ^ TT Pioneers – Early Car Racing in the Isle of Man by Robert Kelly p68 The Manx Experience (1996) The Alden Press ISBN No 1 873120 61 3
- ^ The Motor Cycle pp545 dated 19 June 1905
- ^ Island Racer 2003 p89 Mortons Media Group Ltd ISBN 0954244222
- ^ 2015 International Tourist Trophy Regulations page 22 ACU Events Isle of Man Limited (2015) Isle of Man Department of Economic Development
- ^ 2015 International Tourist Trophy Regulations ACU Events Isle of Man Limited page 5 and page 58 Appendix A
- ^ 2015 International Tourist Trophy Regulations page 2 & Appendix C ACU Events Isle of Man Limited
- ^ International Tourist Trophy Regulations 2015 page 5/Appendix D page 34 ACU Events (Isle of Man) Limited (2015) Isle of Man Department of Economic Development
- ^ International Isle of Man TT Regulations 2012 page 41-42 Appendix-E ACU Events (Isle of Man) Ltd (2012) Isle of Man Department of Economic Development
- ^ 2019 Technical Regulations International Isle of Man Tourist Trophy page 131 & 135 Appendix E Lightweight TT Technical Regulations. ACU Events (Isle of Man) Limited (2019) Isle of Man Department of Economic Development.
- ^ Motocourse History of the Isle of Man TT Races 1907–1989 page 18-19 and 23 (Mick Woollett Technical Notes) Nick Harris © Hazelton Securities Ltd (1990) Graficas Esatalla SA ISBN 0-905138-71-6
- ^ TT Topics and Tales by David Wright – Amulree Publications (4 April 2006) ISBN 1901508099
- ^ 2010 International Tourist Trophy Regulations page 2 ACU Events Isle of Man Limited
- ^ REGULATIONS TT ZERO – 2010 International Tourist Trophy – Isle of Man 29 May – 11 June p27 ACU Events Ltd (2010)
- ^ "History is made in the 2012 SES TT Zero". iomtt.com. 6 June 2012. Retrieved 24 May 2015.
- ^ 1947 TT races, overview IoM TT.com. Retrieved 26 September 2015
- ^ 1950 Clubman TT 1000 cc class results IoM TT.com. Retrieved 26 September 2015
- ^ a b Motor Cycle, 9 March 1967, pp.284–286 Roadsters on the Magic Lap. A Production-TT Recce in Manxland by David Dixon. Accessed 26 September 2015
- ^ 1956 Clubman TT Junior class results IoM TT.com. Retrieved 26 September 2015
- ^ 1956 Clubman TT Senior class results IoM TT.com. Retrieved 26 September 2015
- ^ 1963 Senior race results, Competitor Ray Knight, Hughes Triumph Archived 4 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine, Manx Grand Prix.Org official website, Retrieved 19 October 2015
- ^ 1964 Senior race results, Competitor Ray Knight, Hughes Triumph Archived 4 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine, Manx Grand Prix.Org official website, Retrieved 19 October 2015
- ^ Ray Knight, Competitor Profile, IoM TT.com official website, Retrieved 19 October 2015
- ^ Motor Cyclist Illustrated, January 1965, p.41 More Production racing. Accessed 19 October 2015
- ^ The Guardian page 9 Wednesday 8 June 1927
- ^ Mona's Herald page 5 A SAFTEY [sic?] MEASURE Wednesday 14 March 1928
- ^ TT Special Editor G.S. Davison page 4 TT HISTORY IS MADE Friday 11 June 1937
- ^ Manx Independent – Manninagh Seyr pages 62 & 64 TT REVAMP WILL BRING BENEFITS TO ALL Isle of Man Newspapers Ltd (2019) Tindle Newspaper Group – Newsprint (Knowsley) Limited – Thursday 31 October 2019 ISSN 1358-4391 "The 101st edition of the Tourist trophy races will officially start one day later than normal next year on Sunday, May 31."
- ^ TT ROAD RACES 2019 ROADS CLOSED TO THE PUBLIC Isle of Man Department of Infrastructure -Rheynn Arraghey Bun-Troggalys Public Notice (2019)
- ^ Isle of Mann Government announces cancellation of 2020 TT Races Isle of Mann TT 16 March 2020
- ^ Yamaha keep travelling marshals on Road and Track iomtt.com, 29 May 2013. Retrieved 26 September 2020
- ^ TT roads closure notice 2016 Retrieved 1 June 2016
- ^ TVIM, 28 August 2013, Retrieved 12 December 2015
- ^ The Oxford Companion to Sports and Games Edited by John Arlott Oxford University Press (1975) pp. 669 ISBN 0-19-211538-3
- ^ "World's fastest way to die: Motorbike race that's killed 246". News.com.au — Australia's Leading News Site. 2 July 2015.
- ^ Brown, Aaron (7 June 2017). "3 Riders Killed in Separate Incidents at 2017 Isle Of Man TT". The Drive. Retrieved 13 June 2017.
- ^ Backus, Richard (March–April 2017), "ISLE OF MAN", Motorcycle Classics, pp. 50–56
- ^ "Two more motorcyclists killed at Isle of Man TT races". The Telegraph. 11 June 2016. Retrieved 20 February 2017.
- ^ Lieback, Ron (13 June 2016). "2016 Isle of Man TT Recap – Winners & Fatalities". Ultimate MotorCycling. Retrieved 7 February 2017.
- ^ "World's fastest way to die: The most dangerous race on the planet". news.com.au. Retrieved 20 February 2017.
- ^ "Two more deaths take Isle of Man TT Festival toll to five". express.co.uk. Retrieved 20 February 2017.
- ^ Race results, Steve Mercer iomtt.com Retrieved 25 January 2020
- ^ a b Isle of Man TT outlines changes after Mercer course car collision Autosport, 18 April 2019, Retrieved 26 January 2020
- ^ Isle of Man TT 2018: Injured Steve Mercer thanks fans for support BBC News, 5 December 2018. Retrieved 26 January 2020
- ^ a b c TT organisers refuse to reveal contents of serious crash investigation BBC News, 7 December 2018. Retrieved 26 January 2020
- ^ Stricken Isle of Man TT racer Steve Mercer says 'it can't end like this' Belfast Newsletter, 9 April 2019. Retrieved 26 January 2020
- ^ a b Mercer crash report still unavailable one year on bikesportnews, 10 June 2019. Retrieved 26 January 2020
- ^ Derbyshire, Adrian (6 June 2018). "What we know so far about Mercer's crash". Isle of Man Today. Tindle Newspapers Ltd. Retrieved 26 January 2020.
- ^ Newsdesk (31 May 2018). "Red flag procedure with immediate effect". Isle of Man Today. Tindle Newspapers Ltd. Retrieved 26 January 2020. [ permanent dead link ]
- ^ White, Kyle (18 June 2018). "TT 2018: Ex-Motorsport Association chief will lead independent inquiry into Steve Mercer incident". The News Letter. Johnston Publishing (NI). Retrieved 26 January 2020.
- ^ Steve Mercer denied access to official report into head-on collision at Isle of Man TT Belfast Newsletter, 11 April 2019. Retrieved 26 January 2020
- ^ They won't even tell Mercer what went wrong iomtoday, 5 April 2019. Retrieved 26 January 2020
- ^ Steve Mercer's compensation claim in wake of TT course car crash 'must be heard in Isle of Man' Belfast Newsletter, 29 August 2019. Retrieved 26 January 2020
- ^ ACU TT Statement Auto Cycle Union, 18 April 2019. Retrieved 26 January 2020
- ^ TT bosses outline safety changes following Mercer crash bikesportnews, 18 April 2019 Retrieved 27 January 2020
- ^ ACU official stands down in tracker row iomtoday.co.im, 6 September 2019. Retrieved 27 January 2020
- ^ https://www.iomtt.com/tt-database/events?meet_code=TT01%20%20&era=#:~:text=TT%202001,%2D1918%20and%201939%20%2D%201945.[ bare URL ]
- ^ https://www.iomtt.com/news/2020/03/16/tt-2020-cancelled[ bare URL ]
- ^ https://www.iomtt.com/news/2020/05/04/classic-tt-2020-cancelled[ bare URL ]
- ^ https://www.iomtt.com/news/2020/12/04/tt-2021-cancellation[ bare URL ]
- ^ https://www.iomtt.com/news/2021/03/04/tt-2022[ bare URL ]
- ^ The true cost of cancelling the Isle of Man TT goes far beyond losing racing's ultimate adrenaline rush The Independent, 2 April 2020. Retrieved 23 April 2021
- ^ "Competitor Analysis". Isle of Man TT. Duke Marketing Limited. Retrieved 3 June 2018.
- ^ Records reported are lap times achieved during races only. Except where otherwise noted, sourcing in this table is from the IOMTT.COM website: title=IOM TT: Current Isle of Man TT Lap Records
- ^ a b c "RST Superbike TT – Result Sheet" (PPDF). Isle of Man TT. Duke Marketing Limited. 2 June 2018. Retrieved 3 June 2018.
- ^ a b "Monster Energy Supersport TT 1 – Result Sheet" (PDF). Isle of Man TT. Duke Marketing Limited. 4 June 2018. Retrieved 4 June 2018.
- ^ a b "Bennetts Lightweight TT – Result Sheet" (PDF). Isle of Man TT. Duke Marketing Limited. 8 June 2018. Retrieved 8 June 2018.
- ^ a b "PokerStars Senior TT" (PDF). Isle of Man TT. Duke Marketing Ltd. 8 June 2018. Retrieved 8 June 2018.
- ^ a b c d "RL360 Superstock TT – Result Sheet" (PDF). Isle of Man TT. Duke Marketing Limited. 4 June 2018. Retrieved 4 June 2018.
- ^ a b "Excellent stuff by @michaelrutter_ with a win at 121.9mph and @jm130tt 2nd at over 120mph and a top speed of 176mph o Sulby straight". 6 June 2019.
- ^ a b c "Locate.im Sidecar TT 2" (PDF). Isle of Man TT. Duke Marketing Limited. 8 June 2018. Retrieved 8 June 2018.
- ^ "Monster Energy Supersport TT 2 – Result Sheet" (PDF). Monster Energy. 8 June 2018. Retrieved 8 June 2018.
- ^ "2015 Bennetts Lightweight TT results" (PDF). IOMTT.COM.
- ^ "Monster Energy Supersport TT 2 – Result Sheet" (PDF). Isle of Man TT. Duke Marketing Ltd. 8 June 2016. Retrieved 11 June 2016.
- ^ a b c "Isle of Man TT: Hickman wins thriller, smashes lap record". Isle of Man TT. Duke Marketing Ltd. 8 June 2018. Retrieved 8 June 2018.
- ^ a b c "Birchalls on form in Sure Sidecar TT Race 2". Isle of Man TT. Duke Marketing Ltd. 10 June 2016. Retrieved 11 June 2016.
Holden/Winkle were secure in second and with the runners-up spot, they took the overall Sidecar Championship with Reeves/Farrance salvaging their TT race week with another podium.
- ^ a b "PokerStars Senior TT – Result Sheet" (PDF). Isle of Man TT. Duke Marketing Ltd. 10 June 2016. Retrieved 11 June 2016.
- ^ "The Isle of Man TT Website - Dwight Mitchell Interview". www.ttwebsite.com . Retrieved 12 December 2020.
- ^ "The Isle of Man TT Website". www.ttwebsite.com . Retrieved 12 December 2020.
- ^ "Mitchell Heading For Isle Of Man On MV F4". Roadracing World Magazine | Motorcycle Riding, Racing & Tech News. 3 May 2002. Retrieved 12 December 2020.
- ^ Mitchell, Dwight (1 February 2000). "American Motorcyclist". American Motorcyclist : The Monthly Journal of the American Motorcyclist Association. Pickerington, OH 43147: American Motorcyclist Assocication: 61. ISSN 0277-9358. CS1 maint: location (link)
- ^ Senior TT – Isle of Man TT 25 May – 7 June 2019 Positions Lap Order page 6 Clerk of the Course Gary Thompson ACU Events Ltd (2019) Isle of Man Department for Enterprise
- ^ IoM TT.com, News, 28 December 2012 Retrieved 14 September 2015
- ^ TT News Race Edition #2 2012 page 20 Isle of Man Newspapers Ltd (2012) Bridson & Horrox Ltd
- ^ TT Supporters Club Magazine – Winter 2012 page 15 (2012) TT Supporters Club
- ^ TT News Race Edition #3 2014 page 23 Isle of Man Newspapers Ltd (2014) Bridson & Horrox Ltd
- ^ TT Supporters Club Magazine – Summer 2015 page 10 (2015) TT Supporters Club
- ^ TT Supporters Club Magazine – Winter 2015 page 13 (2015) TT Supporters Club
- ^ TT Supporters Club Magazine – Winter 2016 page 22 (2016) TT Supporters Club
- ^ TT Supporters Club Magazine – Summer 2018 page 17 (2018) TT Supporters Club
- ^ TT News Issue One 2019 page 27 25 May 2019 Isle of Man Newspapers Ltd (2019) Bridson & Horrox Ltd
- ^ "Manx TT Super Bike Review".
- ^ "Review: 'TT Isle of Man–Ride on the Edge 2' is Your Ticket to the Race Canceled by Coronavirus".
- ^ "The Isle of Man TT is Coming to Your Game Room".
References [edit]
- Barker, Stuart (2007). 100 One Hundred Years of the TT. EMAP ISBN 1-84605-235-1
- Duckworth, Mick (2007). TT 100 – The Authorised History of the Isle of Man Tourist Trophy Racing. Lily Publications ISBN 9781899602674
- Harris, Nick (1991). Motocourse History of the Isle of Man Tourist Trophy Races 1907–1989 Hazelton Publishing ISBN 0-905138-71-6
- Mac McDiarmid (2004). The Magic of The TT. A Century of Racing over The Mountain Haynes Publishing. ISBN 1-84425-002-4
- Noyes, Denis (1999) 50 Years of Moto Grand Prix. Hazelton Publishing Ltd ISBN 1-874557-83-7
- Pidcock, Fred & Snelling, Bill (2007) History of the Isle of Man Clubman's TT Races 1947–1956. Amulree Publications ISBN 1-901508-10-2
- Savage, Mike (1997) TT Heroes. Amulree Publications ISBN 0-9521126-9-8
- Snelling, Bill (1996). The Tourist Trophy in Old Photographs Collected by Bill Snelling. Sutton Publishing ISBN 1-84015-059-9
- Stroud, Jon (2007). The Little Book of the TT. Green Umbrella Publishing ISBN 1-905828-24-1
- Wright, David (2007). 100 Years of the Isle of Man TT Races. A Century of Motorcycle Racing. Crowood Press ISBN 1-86126-906-4
- Wright, David (2006). TT Topics and Tales. Amulree Publications ISBN 1-901508-09-9
External links [edit]
- Official website by IoM Department for Enterprise
- Alternative website by Duke Marketing
- Route of Isle of Man TT (Google Maps)
- Motorcycle Classics article on the 100th anniversary of the Isle of Man TT
- Video of TT Access Road traffic TVIM
Coordinates: 54°10′02″N 4°28′44″W / 54.16722°N 4.47889°W / 54.16722; -4.47889
What Does Tt Isle of Man Stand for
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Isle_of_Man_TT
0 Response to "What Does Tt Isle of Man Stand for"
Post a Comment